The Smarter Thinking Profile
The Smarter Thinking Profile measures performance areas and beliefs. Specifically patterns of rigid, extreme, and illogical beliefs in relation to performance.
By accurately measuring these beliefs, we can recognise and address these often deeply held attitudes to performance. This allows us to take responsibility for how we think about, and react to, a range of performance situations.
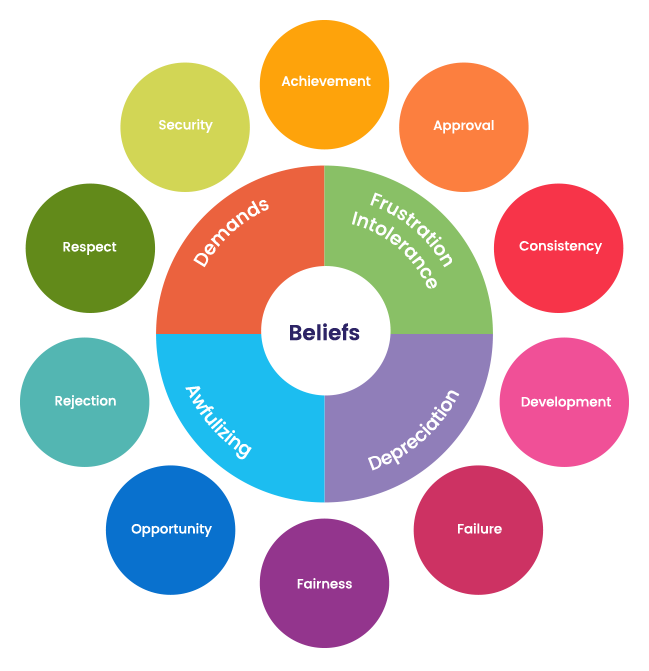
The questions on the Smarter Thinking Profile are in relation to 10 distinct performance areas you may encounter. Each of the 10 performance areas represents a distinct aspect of the world in which you perform.
The 10 performance areas are:
Achievement
Reflects your attitudes about reaching your goals, and success.
Approval
Reflects your attitudes about being viewed favourably by others.
Consistency
Reflects your attitudes about your normal working routines.
Development
Reflects your attitudes about making continual progress.
Failure
Reflects your attitudes about not reaching your goals.
Fairness
Reflects your attitudes about being treated fairly by others.
Opportunity
Reflects your attitudes about being given the chances to progress.
Rejection
Reflects your attitudes about being dismissed by others.
Respect
Reflects your attitudes about being treated with consideration.
Security
Reflects your attitudes about the safety of your position.
For example, we know that wanting to achieve goals, to gain approval, and to be respected is important in most performance environments.
However, when these ‘wants’ become ‘musts’ individuals can put too much pressure on themselves, and can become distressed when these wants and musts are not met.
Also, when the prospect of not having your wants and musts met is followed by beliefs that it is ‘terrible’, and that you ‘cannot stand it’, and that you are ‘a failure’, you are more likely to feel, think, and act in ways that hinder you from reaching your performance goals.
For each of the 10 performance areas, we measured 4 types of beliefs that reflect rigid, extreme, and illogical ways of thinking.
What are the 4 types of beliefs?
Demands
Rigid and dogmatic beliefs that include “must”, “ought to”, “absolutely should”, or “have to”. Reflects the tendency to demand the things that we want.
Frustration Intolerance
Beliefs that include “can’t stand”, “can’t bear”, or “can’t tolerate”. Reflects the tendency to conclude that it is intolerable to not get the things we want.
Awfulizing
Beliefs that include “awful”, “terrible”, “appalling”, or “horrible”. Reflects the tendency to over-exaggerate the consequences of not getting the things we want.
Depreciation
Beliefs that include “worthless”, “no good”, “failure”, “unlikable”, “loser”, or “useless”. Reflects the tendency to negatively label ourselves as a whole, as a result of not getting the things we want.
Get your FREE profile report
The Smarter Thinking Profile measures patterns of rigid, extreme, and illogical beliefs in relation to performance to allow you to recognise and address attitudes to performance.
As the diagram suggests, the Smarter Thinking profile measures each of the 4 belief types across all 10 performance areas.